Programming in natural language
Jaak Henno, Tallinn University of Technology, Estonia
Hannu Jaakkola, Tampere University, Pori, Finland
Jukka Mäkelä, University of Lapland, Finland
This presentation is on-line at http://staff.ttu.ee/~jaak.henno/conf2025/index_min.htm
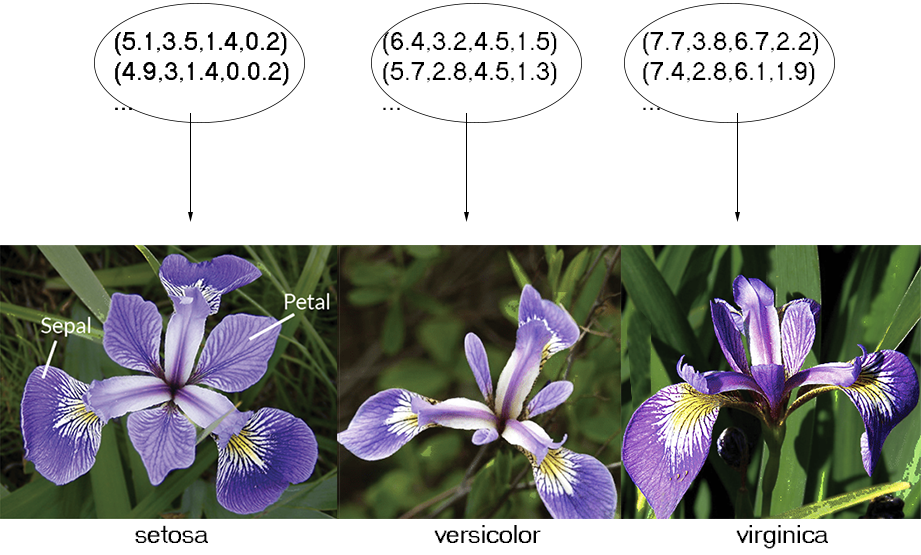
For processing (big) DATA are increasingly used programs based on Large Language Models (LLM), e.g. the chatGPT
These programs can produce fluent text on several natural languages (English, Estonioan, Finnish Croatian....)
Although these 'fluent chatterers' do not understand a word what they output - they are also able to create (simple) computer programs
1. To chatGPT-s was given the task description, e.g. Create a Python program illustrating software project statistics...
|
chatGPT outputs a Python program, which we execute |
|
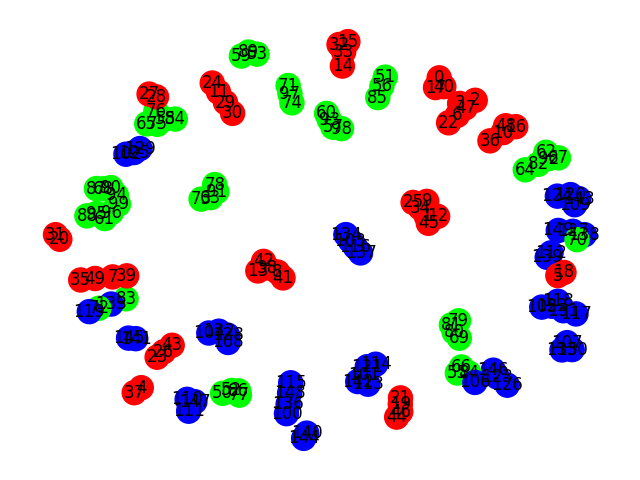
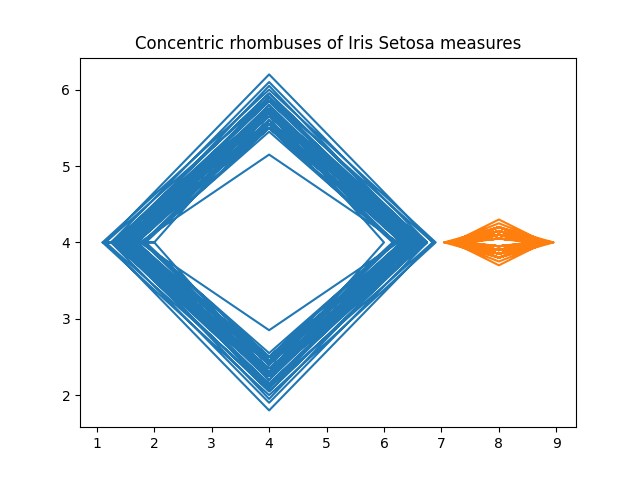
Import list of items from the uploaded file iris_col_dat.py, calculate distances between list items using the first four elements of lists, create graph of items connecting items with minimal distance, color the graph nodes using the last element of the item as an RGB-triple |
|
All items from the same Fisher's cluster appered as 42 connected components, but 42 - this is not information compression |
|
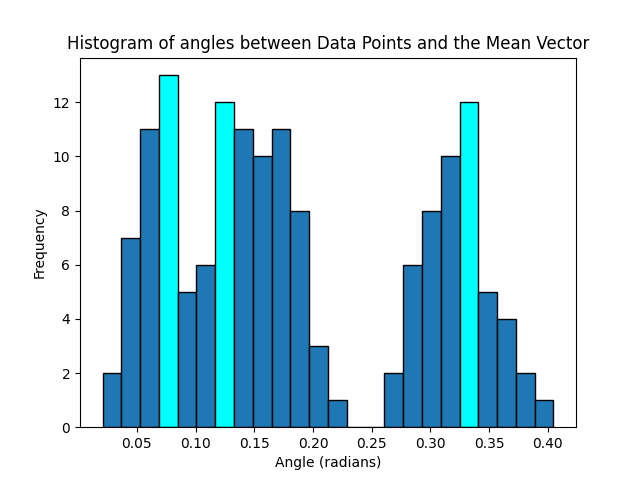
Vectors similarity appears as minuscule angles between them. To get overview we asked chatGPT to create histogram of angles between items and a fixed vector - the average of all data vectors.
|
"Create a Python 3 program, which imports from the file iris_col_dat.py the list items, finds the mean of the list and creates a histogram with 24 bins of angles of lists of first four components of lists with the mean; set color of 3 locally maximal bins of the histogram to 'aqua'." |
|
Expectation of items in three local maximums were added to the list of items as new 'centers of attraction' |
|
|
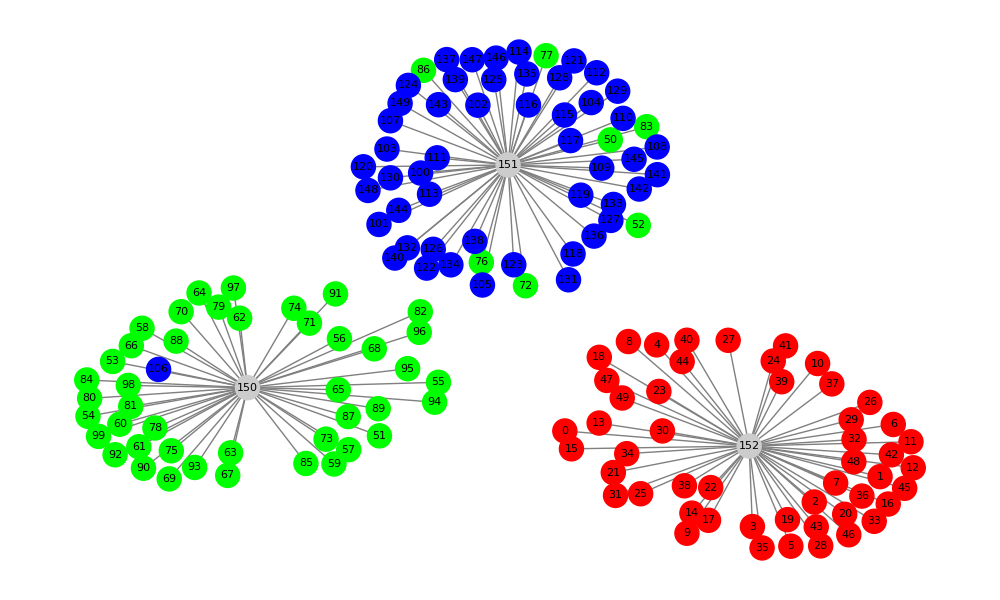
Create a Python 3 program, which imports from the file iris_col_dat.py the list of lists Items, using the first 4 items as coordinates finds for each list except the last three distances of the list with the last three lists, finds the minimal distance among these three distances, creates a graph whose nodes are lists from the list Items; for each node except the last thee add edge to node in last three nodes which had minimal distance with the node; color nodes using the last item in the list as the RGB triple for node color |
|
By popular clustering criteria (the Davis-Bouldin-Index, Silhouette score, Calinski-Harabasz Index) this clustering is better than Fisher's |
|
Expressing your ideas directly to computer forces humans to be more precise. This would improve requirements, involve users, improve communication between users and developers, create better process planning and definition of final goals
But answers provided by chatGPT-s should never be accepted as truths before careful testing